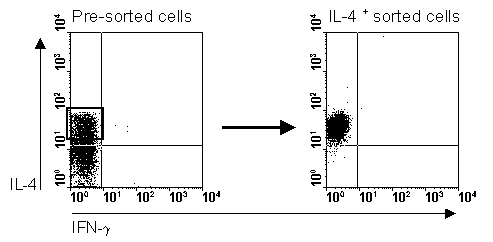
Fig.1. CD4+ T cells stimulated for 3 hours with PMA/ionomycin, labeled
with the secretion assay, 15 min. secretion time (left part of figure) and
sorted on a FACSVantage (right part of figure) Published in: H.H.Smits et al.
Eur.J.Imm. Vol 31, 1055 - 1065 (2001)